Gentle Parenting for Children’s Development
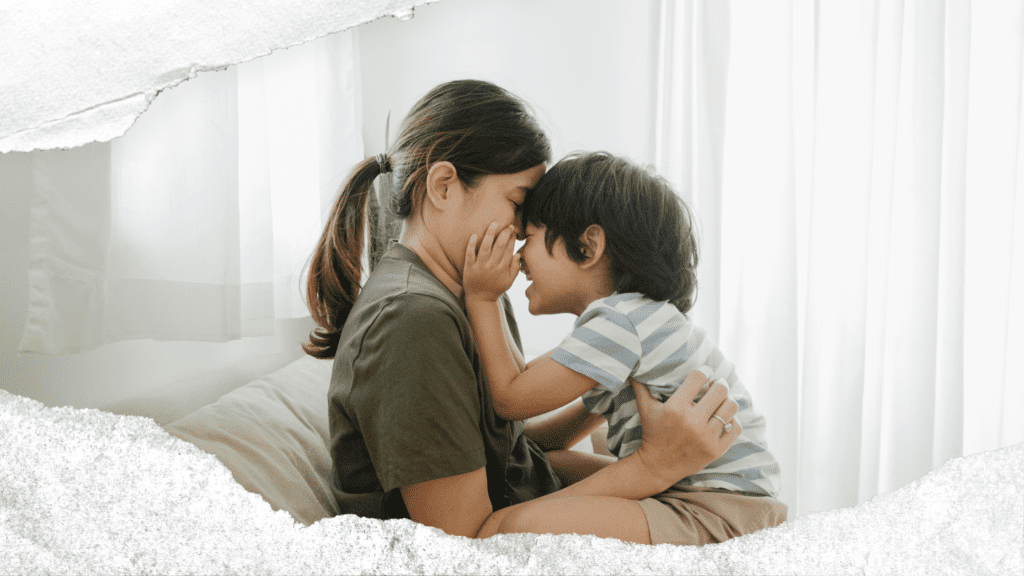


The concept of “gentle parenting” is taking center-stage in parenting discussions. It’s not just another trend but a timeless approach that appeals to parents and teachers who want to cultivate a nurturing, empathetic, and respectful environment for children between the ages of 3 to 10. But what exactly does the term gentle parenting mean? How does it differ from other parenting styles?
Gentle parenting isn’t about being ‘soft’ or overly indulgent, contrary to common misconceptions. It refers to a parenting style that mirrors respect, empathy, understanding, and patience. It is a method where the authority lies with the caregivers but is executed with love and respect, without intimidation or fear. This form of parenting encourages parents and teachers to understand the emotions of children and respond rather than react to their behaviors.
Setting Boundaries with Empathy in Gentle Parenting
Setting boundaries with empathy is a crucial aspect of gentle parenting. Fostering a strong connection with your child while guiding them through positive discipline techniques. It’s about understanding your child’s perspective, emotions, and needs, and responding to them with love and empathy.
When setting boundaries, approach it with empathy and understanding. Instead of imposing rules and punishments, gentle parents consider the reasons behind their child’s behavior and communicate with compassion. Here are some tips on how to set boundaries with empathy in gentle parenting:
– Listen to Your Child: Before enforcing boundaries, listen to your child’s thoughts and feelings.
– Validate their emotions and show them you understand where they’re coming from. They will feel heard and respected, making them likely to cooperate.
– Explain the Reasoning: When setting a boundary, explain the reasoning behind it. Help them understand why the rule is in place and how it benefits them and others. This makes them more likely to comply willingly rather than out of fear.
– Use Positive Language: Frame your boundaries in a positive light. For example, instead of saying “Don’t run in the house,” you can say, “Let’s walk slowly inside.” This guides them towards the desired behavior in a constructive way.
Gentle parenting isn’t about being ‘soft’ or overly indulgent, contrary to common misconceptions. It refers to a parenting style that mirrors respect, empathy, understanding, and patience. It is a method where the authority lies with the caregivers but is executed with love and respect, without intimidation or fear. This form of parenting encourages parents and teachers to understand the emotions of children and respond rather than react to their behaviors.
Setting Boundaries with Empathy in Gentle Parenting
Setting boundaries with empathy is a crucial aspect of gentle parenting. Fostering a strong connection with your child while guiding them through positive discipline techniques. It’s about understanding your child’s perspective, emotions, and needs, and responding to them with love and empathy.
When setting boundaries, approach it with empathy and understanding. Instead of imposing rules and punishments, gentle parents consider the reasons behind their child’s behavior and communicate with compassion. Here are some tips on how to set boundaries with empathy in gentle parenting:
– Listen to Your Child: Before enforcing boundaries, listen to your child’s thoughts and feelings.
– Validate their emotions and show them you understand where they’re coming from. They will feel heard and respected, making them likely to cooperate.
– Explain the Reasoning: When setting a boundary, explain the reasoning behind it. Help them understand why the rule is in place and how it benefits them and others. This makes them more likely to comply willingly rather than out of fear.
– Use Positive Language: Frame your boundaries in a positive light. For example, instead of saying “Don’t run in the house,” you can say, “Let’s walk slowly inside.” This guides them towards the desired behavior in a constructive way.
–Offer Choices: Give your child some autonomy by offering them choices within the boundaries you’ve set. This can help them feel empowered and in control of their actions, leading to a more positive response.
– Set Realistic Expectations: Be realistic about the boundaries you set based on your child’s age and developmental stage.
– Avoid setting too many rules or rules that are too rigid, as this can lead to frustration and disconnection.
– Follow Through with Consistency: Consistency is key when it comes to setting boundaries. Stick to the rules you’ve. This helps your child understand the importance of boundaries and the consequences of their actions. By setting boundaries with empathy in gentle parenting, you nurture a strong and loving relationship with your child. Remember empathy and understanding are at the core of gentle parenting, helping your child feel supported and respected as they navigate the world around them.
Nurturing Emotional Intelligence in Children Through Gentle Parenting
Emotional intelligence is one of the most valuable skills that a child can learn early in life. It helps them understand and manage their own emotions,
empathize with the feelings of others, and build strong, healthy relationships.
As a parent or teacher, you play a crucial role in nurturing emotional intelligence in children. Gentle parenting focuses on empathy, respect, and understanding. It promotes positive discipline techniques that prioritize the emotional well-being of the child. By practicing gentle parenting, you create a safe and supportive environment where children feel free to express themselves and learn to regulate their emotions effectively.
Here are some strategies and tips for nurturing emotional intelligence in children through gentle parenting:
– Model Emotional Regulation: Children learn best through observation. By and managing your own emotions, you teach them valuable skills. Show your child how to calmly communicate feelings, take deep breaths when upset, and resolve conflicts peacefully.
– Set Realistic Expectations: Be realistic about the boundaries you set based on your child’s age and developmental stage.
– Avoid setting too many rules or rules that are too rigid, as this can lead to frustration and disconnection.
– Follow Through with Consistency: Consistency is key when it comes to setting boundaries. Stick to the rules you’ve. This helps your child understand the importance of boundaries and the consequences of their actions. By setting boundaries with empathy in gentle parenting, you nurture a strong and loving relationship with your child. Remember empathy and understanding are at the core of gentle parenting, helping your child feel supported and respected as they navigate the world around them.
Nurturing Emotional Intelligence in Children Through Gentle Parenting
Emotional intelligence is one of the most valuable skills that a child can learn early in life. It helps them understand and manage their own emotions,
empathize with the feelings of others, and build strong, healthy relationships.
As a parent or teacher, you play a crucial role in nurturing emotional intelligence in children. Gentle parenting focuses on empathy, respect, and understanding. It promotes positive discipline techniques that prioritize the emotional well-being of the child. By practicing gentle parenting, you create a safe and supportive environment where children feel free to express themselves and learn to regulate their emotions effectively.
Here are some strategies and tips for nurturing emotional intelligence in children through gentle parenting:
– Model Emotional Regulation: Children learn best through observation. By and managing your own emotions, you teach them valuable skills. Show your child how to calmly communicate feelings, take deep breaths when upset, and resolve conflicts peacefully.
– Encourage Emotional Expression: Create an open and supportive atmosphere where your child feels comfortable sharing their emotions. Listen actively, validate their feelings, and help them label and make sense of what they are experiencing. Encourage them to express themselves through art, writing, or storytelling.
– Teach Empathy: Help your child develop empathy by exposing them to diverse perspectives and experiences. Model empathy in your own interactions with others. Help them choose books to read that demonstrate empathy.
–Set Boundaries with Love: Gentle parenting involves setting clear and consistent boundaries while maintaining a loving and respectful attitude. Avoid using harsh discipline or punishment. Focus on positive reinforcement and problem-solving.
– Practice Active Listening: Listen to your child without judgment or interruption. Reflect back their feelings and concerns. By listening, you validate their emotions and build trust in your relationship.
– Promote Problem-Solving Skills: Encourage your child to resolve conflicts independently. Teach them problem-solving strategies, such as brainstorming solutions, considering different perspectives, and seeking compromise. Offer guidance and support as they navigate difficult situations.
By incorporating gentle parenting practices into your interactions with children, you help them develop emotional intelligence skills that serve them throughout their lives. Building emotional intelligence is an ongoing process that requires understanding, and consistent support. Embrace the journey of nurturing your child’s emotional well-being and watch them grow into empathetic, resilient individuals.
Using Positive Discipline Techniques in Gentle Parenting
Positive discipline techniques play a crucial role in gentle parenting, focusing on understanding and responding to children’s needs with empathy and respect. By fostering a loving and supportive environment, gentle parenting aims to build strong relationships between parents and children while promoting positive behavior.
One key approach is to use positive reinforcement to encourage desirable behaviors. This involves praising and rewarding children when they exhibit behavior that aligns with family values and expectations. Positive reinforcement of good behavior fosters a sense of self-esteem and confidence in children.
Another essential element of gentle parenting is setting clear and reasonable boundaries. Children thrive in environments where they know what is expected of them and the consequences of their actions. By establishing consistent rules and limits, parents can provide children with a sense of security and guidance.
– Teach Empathy: Help your child develop empathy by exposing them to diverse perspectives and experiences. Model empathy in your own interactions with others. Help them choose books to read that demonstrate empathy.
–Set Boundaries with Love: Gentle parenting involves setting clear and consistent boundaries while maintaining a loving and respectful attitude. Avoid using harsh discipline or punishment. Focus on positive reinforcement and problem-solving.
– Practice Active Listening: Listen to your child without judgment or interruption. Reflect back their feelings and concerns. By listening, you validate their emotions and build trust in your relationship.
– Promote Problem-Solving Skills: Encourage your child to resolve conflicts independently. Teach them problem-solving strategies, such as brainstorming solutions, considering different perspectives, and seeking compromise. Offer guidance and support as they navigate difficult situations.
By incorporating gentle parenting practices into your interactions with children, you help them develop emotional intelligence skills that serve them throughout their lives. Building emotional intelligence is an ongoing process that requires understanding, and consistent support. Embrace the journey of nurturing your child’s emotional well-being and watch them grow into empathetic, resilient individuals.
Using Positive Discipline Techniques in Gentle Parenting
Positive discipline techniques play a crucial role in gentle parenting, focusing on understanding and responding to children’s needs with empathy and respect. By fostering a loving and supportive environment, gentle parenting aims to build strong relationships between parents and children while promoting positive behavior.
One key approach is to use positive reinforcement to encourage desirable behaviors. This involves praising and rewarding children when they exhibit behavior that aligns with family values and expectations. Positive reinforcement of good behavior fosters a sense of self-esteem and confidence in children.
Another essential element of gentle parenting is setting clear and reasonable boundaries. Children thrive in environments where they know what is expected of them and the consequences of their actions. By establishing consistent rules and limits, parents can provide children with a sense of security and guidance.
Communication is a fundamental aspect of gentle parenting. Open and honest communication between parents and children builds trust and understanding. Listening to children’s thoughts and feelings without judgment helps them feel heard and respected.
In gentle parenting, redirection is often used to address challenging behaviors without resorting to punishment. Instead of focusing on unwanted behavior, parents redirect their attention towards appropriate behaviors. By offering alternative activities, parents’ guide children to positive behaviors while maintaining a peaceful atmosphere.
Emotional regulation is a key component of gentle parenting. Helping children recognize and manage their emotions teaches them essential life skills. By modeling healthy ways to cope with emotions and providing guidance and support, parents help children navigate their feelings in constructive ways.
Overall, gentle parenting emphasizes the importance of building a strong and positive relationship based on empathy, respect, and understanding. Through communication, setting boundaries, positive reinforcement, redirection, and emotional regulation, parents can cultivate a harmonious and connected family dynamic rooted in love and mutual
respect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, practicing gentle parenting is not only beneficial for children but also for parents and the overall family dynamic. By using non- punitive and empathetic approaches, parents foster a strong bond with their children, promote healthy development, and create a nurturing environment
where communication and understanding thrive.
In gentle parenting, redirection is often used to address challenging behaviors without resorting to punishment. Instead of focusing on unwanted behavior, parents redirect their attention towards appropriate behaviors. By offering alternative activities, parents’ guide children to positive behaviors while maintaining a peaceful atmosphere.
Emotional regulation is a key component of gentle parenting. Helping children recognize and manage their emotions teaches them essential life skills. By modeling healthy ways to cope with emotions and providing guidance and support, parents help children navigate their feelings in constructive ways.
Overall, gentle parenting emphasizes the importance of building a strong and positive relationship based on empathy, respect, and understanding. Through communication, setting boundaries, positive reinforcement, redirection, and emotional regulation, parents can cultivate a harmonious and connected family dynamic rooted in love and mutual
respect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, practicing gentle parenting is not only beneficial for children but also for parents and the overall family dynamic. By using non- punitive and empathetic approaches, parents foster a strong bond with their children, promote healthy development, and create a nurturing environment
where communication and understanding thrive.







Responses